A powerful Python package that uses multiple AI agents to debug API failures by analyzing logs, code, and user questions. Built with CrewAI, it supports LLM providers including OpenAI, Anthropic, Google, Ollama, and more.
Watch the multiagent-debugger in action:
The Multi-Agent Debugger uses a sophisticated architecture that combines multiple specialized AI agents working together to analyze and debug API failures.
- Question Analyzer Agent: Extracts key entities from natural language questions and classifies error types
- Log Analyzer Agent: Searches and filters logs for relevant information, extracts stack traces
- Code Path Analyzer Agent: Validates and analyzes code paths found in logs
- Code Analyzer Agent: Finds API handlers, dependencies, and error handling code
- Root Cause Agent: Synthesizes findings to determine failure causes and generates visual flowcharts
- Log Analysis: Enhanced grep, filtering, stack trace extraction, and error pattern analysis
- Code Analysis: API handler discovery, dependency mapping, error handler identification, multi-language support
- Flowchart Generation: Error flow, system architecture, decision trees, sequence diagrams, and debugging storyboards
- Natural Language Processing: Convert user questions into structured queries
- OpenAI
- Anthropic
- Ollama
- Azure OpenAI
- AWS Bedrock
- And 50+ more providers
- Visual Flowcharts: Mermaid diagrams for error propagation and system architecture
- Copyable Output: Clean, copyable flowchart code for easy sharing
- Multi-language Support: Python, JavaScript, Java, Go, Rust, and more
- Structured JSON: Programmatic access to analysis results
- Text Documents: Human-readable reports saved to local files
- Visual Flowcharts: Mermaid diagrams for documentation and sharing
# From PyPI
pip install multiagent-debugger
# From source
git clone https://github.com/VishApp/multiagent-debugger.git
cd multiagent-debugger
pip install -e .- Set up your configuration:
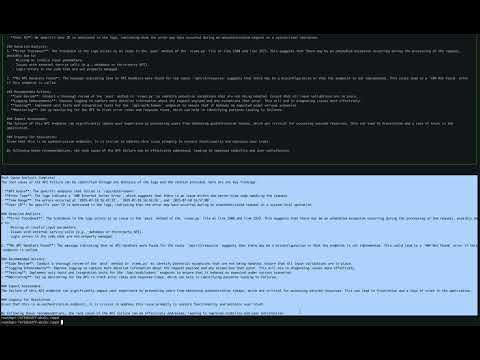
multiagent-debugger setup- Debug an API failure:
multiagent-debugger debug "Why did my /api/users endpoint fail yesterday?"- View generated files:
- Analysis results in JSON format
- Text documents in current directory
- Visual flowcharts for documentation
Usage: multiagent_debugger debug [OPTIONS] QUESTION
Debug an API failure or error scenario with multi-agent assistance.
Arguments:
QUESTION The natural language question or debugging prompt.
Example: 'find the common errors and the root-cause'
Options:
-c, --config PATH Path to config file (YAML)
-v, --verbose Enable verbose output for detailed logs
--mode [frequent|latest|all] Log analysis mode:
frequent: Find most common error patterns
latest: Focus on most recent errors
all: Analyze all available log lines
--time-window-hours INT Time window (hours) for log analysis
--max-lines INT Maximum log lines to analyze
--code-path PATH Path to source code directory/file for analysis
-h, --help Show this message and exit
Examples:
multiagent-debugger debug 'find the common errors and the root-cause' \
--config ~/.config/multiagent-debugger/config.yaml --mode latest
multiagent-debugger debug 'why did the upload to S3 fail?' \
--mode frequent --time-window-hours 12 \
--code-path /Users/myname/myproject/src
multiagent-debugger debug 'analyze recent errors' \
--code-path /path/to/specific/file.py
This command analyzes your logs, extracts error patterns and code paths, and provides root cause analysis with actionable solutions and flowcharts.
Create a config.yaml file (or use the setup command):
# Paths to log files
log_paths:
- "/var/log/myapp/app.log"
- "/var/log/nginx/access.log"
# Path to source code directory or file for analysis (SECURITY FEATURE)
code_path: "/path/to/your/source/code" # Restricts code analysis to this path only
# Log analysis options
analysis_mode: "frequent" # frequent, latest, all
time_window_hours: 24 # analyze logs from last N hours
max_lines: 10000 # maximum log lines to analyze
# LLM configuration
llm:
provider: openai # or anthropic, google, ollama, etc.
model_name: gpt-4
temperature: 0.1
#api_key: optional, can use environment variable
# Phoenix monitoring configuration (optional)
phoenix:
enabled: true # Enable/disable Phoenix monitoring
host: "localhost" # Phoenix host
port: 6006 # Phoenix dashboard port
endpoint: "http://localhost:6006/v1/traces" # OTLP endpoint for traces
launch_phoenix: true # Launch Phoenix app locally
headers: {} # Additional headers for OTLPThe code_path configuration is a security feature that restricts code analysis to a specific directory or file:
# Security: Only analyze code within this path
code_path: "/Users/myname/myproject/src"How it works:
- When logs contain file paths (from stack traces, errors), the system validates them against
code_path - Files outside the configured path are rejected and not analyzed
- This prevents the system from analyzing sensitive system files or unrelated codebases
- Can be a directory (analyzes all source files within) or a specific file
Use cases:
- Multi-project environments: Restrict analysis to current project only
- Security: Prevent analysis of system files or sensitive directories
- Focus: Analyze only specific parts of large codebases
CLI override:
# Override config file code_path for this session
multiagent-debugger debug "question" --code-path /path/to/specific/projectThe system supports various LLM providers including OpenRouter, Anthropic, Google, and others. See Custom Providers Guide for detailed configuration instructions.
Set the appropriate environment variable for your chosen provider:
- OpenAI:
OPENAI_API_KEY - Anthropic:
ANTHROPIC_API_KEY - Google:
GOOGLE_API_KEY - Azure:
AZURE_OPENAI_API_KEY,AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT - AWS:
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID,AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY,AWS_REGION - See documentation for other providers
- Extracts key information like API routes, timestamps, and error types
- Classifies the error type (API, Database, File, Network, etc.)
- Structures the query for other agents
- Searches through specified log files using enhanced grep
- Filters relevant log entries by time and pattern
- Extracts stack traces and error patterns
- Dynamically extracts code paths (file paths, line numbers, function names)
- Validates code paths found in logs
- Validates that extracted file paths are within the configured
code_path(security) - Locates relevant API handlers and endpoints
- Identifies dependencies and error handlers
- Maps the code structure and relationships
- Supports multiple programming languages (Python, JavaScript, Java, Go, Rust, etc.)
- Rejects analysis of files outside the configured code path
- Synthesizes information from all previous agents
- Determines the most likely cause with confidence levels
- Generates creative narratives and metaphors
- Creates visual flowcharts for documentation
- Structured JSON for programmatic access
- Human-readable text documents
- Visual flowcharts in Mermaid format
- Copyable flowchart code for easy sharing
The debugger includes built-in Phoenix monitoring for tracking agent execution, LLM usage, and performance metrics.
multiagent-debugger phoenixThis shows your Phoenix configuration and provides instructions for accessing the dashboard.
When running the debugger on a remote server, use SSH port forwarding to access the Phoenix dashboard:
# On your local machine, create SSH tunnel
ssh -L 6006:localhost:6006 user@your-server
# Then visit in your local browser
http://localhost:6006Phoenix monitoring is configured in your config.yaml:
phoenix:
enabled: true
host: localhost
port: 6006
launch_phoenix: true- Real-time Monitoring: Track agent executions as they happen
- LLM Usage Tracking: Monitor token usage and costs across providers
- Performance Metrics: Analyze execution times and success rates
- Visual Traces: See the complete flow of agent interactions
- Automatic Launch: Starts automatically when you run debug commands
multiagent-debugger list-providersmultiagent-debugger list-models openaimultiagent-debugger debug "Question?" --config path/to/config.yamlmultiagent-debugger debug "What went wrong?" --mode latest --time-window-hours 2multiagent-debugger debug "Find patterns" --max-lines 50000# Only analyze code within /path/to/project directory
multiagent-debugger debug "What caused the error?" --code-path /path/to/project
# Analyze only a specific file
multiagent-debugger debug "Debug this file" --code-path /path/to/file.py# Create virtual environment
python package_builder.py venv
# Install development dependencies
python package_builder.py install
# Run tests
python package_builder.py test
# Build distribution
python package_builder.py dist- Python: 3.8+
- Dependencies:
- crewai>=0.28.0
- pydantic>=2.0.0
- And others (see requirements.txt)
MIT License - see LICENSE for details.
Contributions are welcome! Please feel free to submit a Pull Request.
- GitHub Issues: Report a bug
- Documentation: Read more
- API Debugging: Quickly identify why API endpoints are failing
- Production Issues: Analyze logs and code to find root causes
- Error Investigation: Understand complex error chains and dependencies
- Documentation: Generate visual flowcharts for error propagation
- Team Collaboration: Share analysis results in multiple formats
- Multi-language Projects: Support for Python, JavaScript, Java, Go, Rust, and more
- Time-based Analysis: Focus on recent errors or specific time periods
- Large Log Analysis: Handle massive log files with configurable limits